Earth Observation Research
In Earth Observation Research, we use remote sensing techniques to obtain information on the carbon and water cycles, as well as the state and changes of the atmosphere and cryosphere.
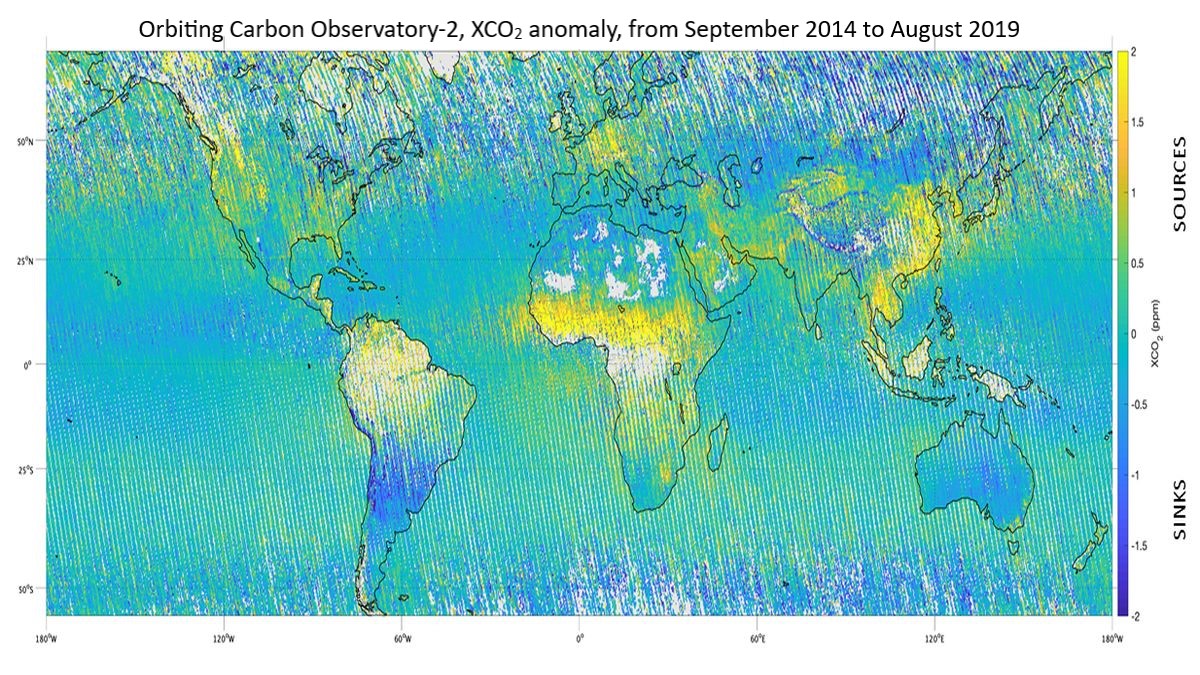
We develop advanced data interpretation methodologies to monitor carbon sequestration, carbon balance, atmospheric composition, air quality, ozone, UV radiation, ground frost, snow mass and snow cover extent.
One cross cutting topic for our group is the Arctic-Boreal Zone, where warming surface temperatures are reducing the extent of snow cover, snow mass, seasonal and permafrost, and ice cover.
These changes are linked to carbon sinks and sources through the ecosystem-atmosphere feedback processes.
More information on the research group web pages: Cryospheric Processes, Atmospheric Remote Sensing and Greenhouse Gases and Satellite Methods, and on the Space and Earth Observation Centre FMI-SPACE website.
