Greenhouse Gases and Satellite Methods
In Greenhouse Gases and Satellite Methods group, we study the distribution of atmospheric greenhouse gases through space-based and ground-based remote sensing. Essential activities of the group include Arctic-boreal satellite Cal/Val activities, development of various GHG emission estimation methods utilizing satellite-, drone and ground-based measurements and studying of the atmospheric radiative transfer. In addition, we use machine learning for data augmentation methods and to study explainability of atmospheric variables. The group is based in Helsinki and Sodankylä.
Central activities of the group:
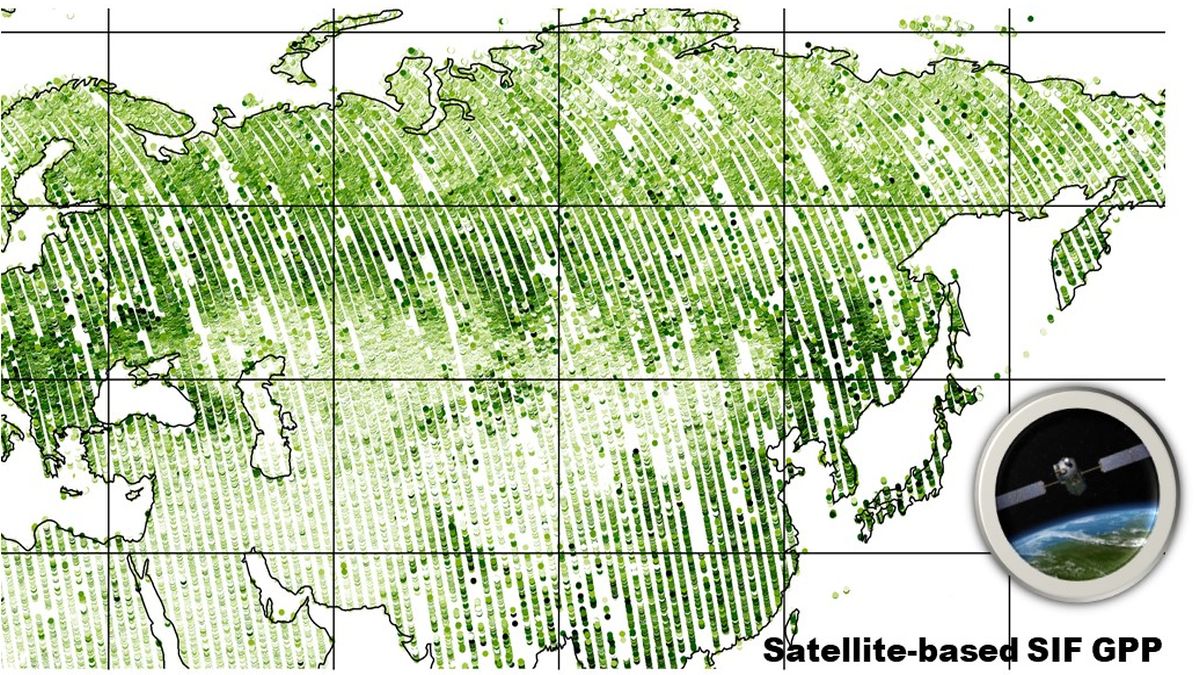
Satellite data analysis from GHG and SIF space missions (S5P TROPOMI, OCO-2 & -3, GOSAT)
We develop and utilise extensive ground-based greenhouse gas and vegetation photosynthesis measurements at Sodankylä in Northern Finland.
These measurements provide an essential validation source for increasing volumes of satellite observations at high latitudes, e.g.
One of our focus areas is to develop methods for satellite-data driven estimations of greenhouse gas sources and sinks.
We also investigate and develop mathematical methods for time series analysis, data assimilation, data fusion, and satellite data interpretation, including uncertainty quantification.
Group participates in two Research Council of Finland flagships: Atmosphere and Climate Competence Center ACCC and Flagship of Advanced Mathematics for Sensing, Imaging and Modelling FAME.
